13.9. EXERCISES 329
Hint: The eigenvalues are 2,1,0.
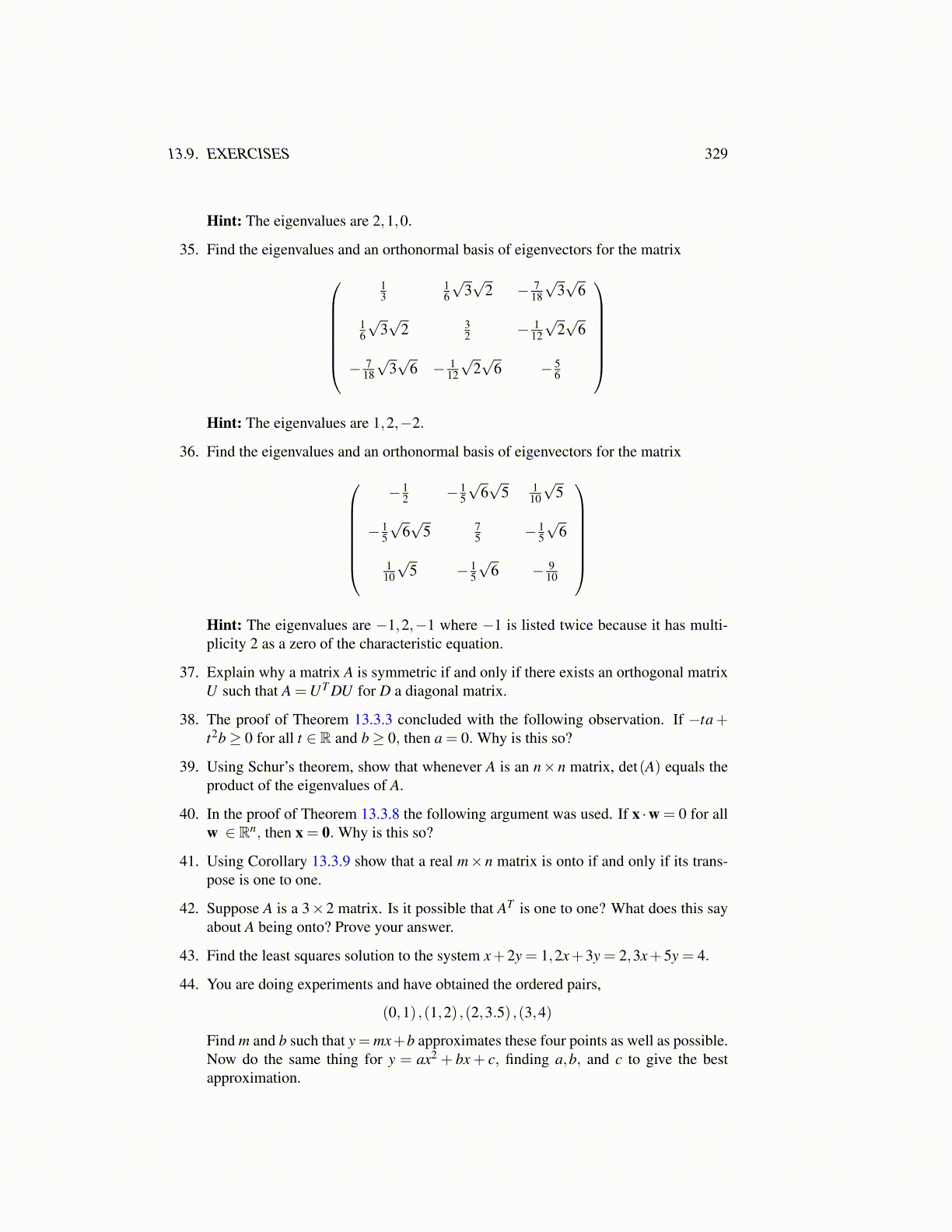
35. Find the eigenvalues and an orthonormal basis of eigenvectors for the matrix
13
16
√3√
2 − 718
√3√
6
16
√3√
2 32 − 1
12
√2√
6
− 718
√3√
6 − 112
√2√
6 − 56
Hint: The eigenvalues are 1,2,−2.
36. Find the eigenvalues and an orthonormal basis of eigenvectors for the matrix− 1
2 − 15
√6√
5 110
√5
− 15
√6√
5 75 − 1
5
√6
110
√5 − 1
5
√6 − 9
10
Hint: The eigenvalues are −1,2,−1 where −1 is listed twice because it has multi-plicity 2 as a zero of the characteristic equation.
37. Explain why a matrix A is symmetric if and only if there exists an orthogonal matrixU such that A =UT DU for D a diagonal matrix.
38. The proof of Theorem 13.3.3 concluded with the following observation. If −ta+t2b≥ 0 for all t ∈ R and b≥ 0, then a = 0. Why is this so?
39. Using Schur’s theorem, show that whenever A is an n×n matrix, det(A) equals theproduct of the eigenvalues of A.
40. In the proof of Theorem 13.3.8 the following argument was used. If x ·w = 0 for allw ∈ Rn, then x = 0. Why is this so?
41. Using Corollary 13.3.9 show that a real m×n matrix is onto if and only if its trans-pose is one to one.
42. Suppose A is a 3×2 matrix. Is it possible that AT is one to one? What does this sayabout A being onto? Prove your answer.
43. Find the least squares solution to the system x+2y = 1,2x+3y = 2,3x+5y = 4.
44. You are doing experiments and have obtained the ordered pairs,
(0,1) ,(1,2) ,(2,3.5) ,(3,4)
Find m and b such that y = mx+b approximates these four points as well as possible.Now do the same thing for y = ax2 + bx + c, finding a,b, and c to give the bestapproximation.